Juan Donicelli, Country Manager of Glencore Copper Argentina, presented the overview of MARA and El Pachón, as well as the expectations of the communities surrounding two of Argentina's major copper projects.
By Panorama Minero

The quest for environmentally friendly technologies has propelled the demand for copper, while the long-term supply outlook remains constrained. Has the time come to accelerate further in MARA and El Pachón?
Global copper demand stands at around 26 million tons, a figure expected to double by 2050. This surge in demand is primarily driven by the need for an energy transition, which will be achieved through renewable energies, storage batteries, and electric vehicles—all of which require copper for electricity transmission. Glencore prioritizes investment in metals that support the transition to a low-carbon economy. In this regard, the growth of the copper sector is pivotal for the company. We are convinced that developing copper projects in the country presents a significant opportunity not only for our company but also for Argentina and the world.
Regarding the previous question, how do you assess the macroeconomic environment for Glencore to further advance in the mentioned projects?
World-class projects like El Pachón and MARA require, anywhere in the world, competitiveness, certainty, and stability in conditions, regulations, and applicable tax burdens, among other aspects, due to the level of investment and commitment they entail. These factors significantly impact the feasibility outcome of projects vying for capital. We are confident that these and other issues can be addressed to promote the realization of these projects, which are so beneficial for the country, as they generate foreign exchange and genuine employment, foster the development of the value chain, and create opportunities for young people and the rest of the community to have a future in their places of origin.
Is applying the know-how from Bajo de la Alumbrera a decisive factor in making a definitive decision on MARA?
Glencore possesses extensive institutional knowledge of MARA and the jurisdiction, based on its management of the Bajo de la Alumbrera operation prior to the integration, in 2020, of the plant and infrastructure of that mine with the Agua Rica deposit. Having this know-how is fundamental for understanding the challenges and peculiarities of the project.
In technical terms, what is required in MARA beyond utilizing the existing infrastructure at Bajo de la Alumbrera?
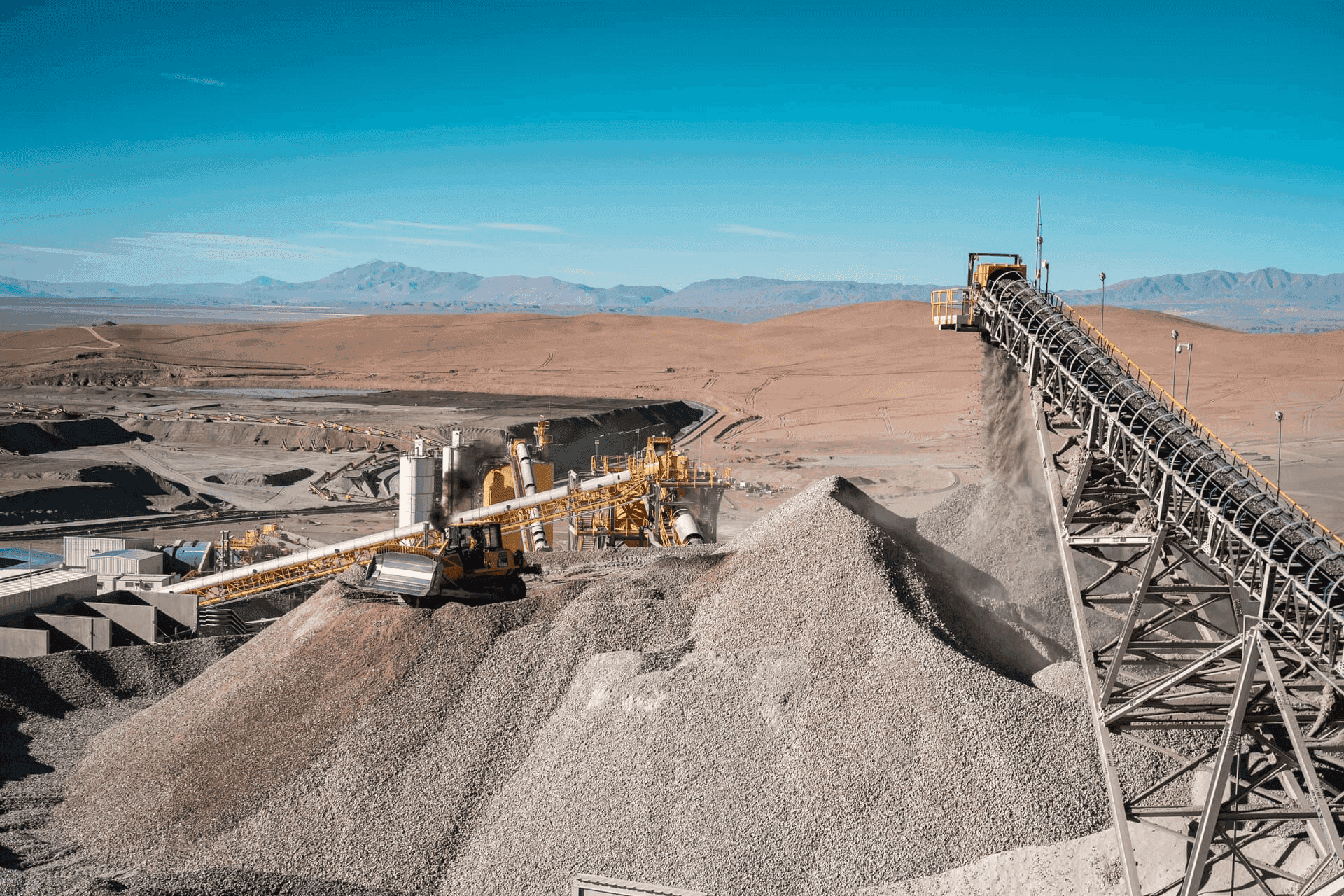
MARA is in the feasibility stage to evaluate the best development options for the project. We are reviewing and updating the study plan and schedule to complete it following the acquisition and understand the steps to advance in the subsequent phases of the project, respecting the high international standards we apply at Glencore.
What is the level of acceptance of the mining industry in the areas of influence of MARA?
Mining is one of the main activities in Catamarca, particularly highlighted in recent years since the completion of Alumbrera in 2018, with the start of several lithium projects in the province. Particularly in the MARA influence zone, in the departments of Andalgalá, Belén, and Santa María, through perception studies, we have seen that one of the main demands of society is the creation of quality job opportunities for residents, both directly and as service providers. Undoubtedly, local communities as a whole see the future of MARA as a great development opportunity, which is also reflected in the growing positive expectations towards the project following the integration of Agua Rica with Alumbrera in 2020.
In the case of El Pachón, considering the decades of experience gained, how would you define its current situation and near future?
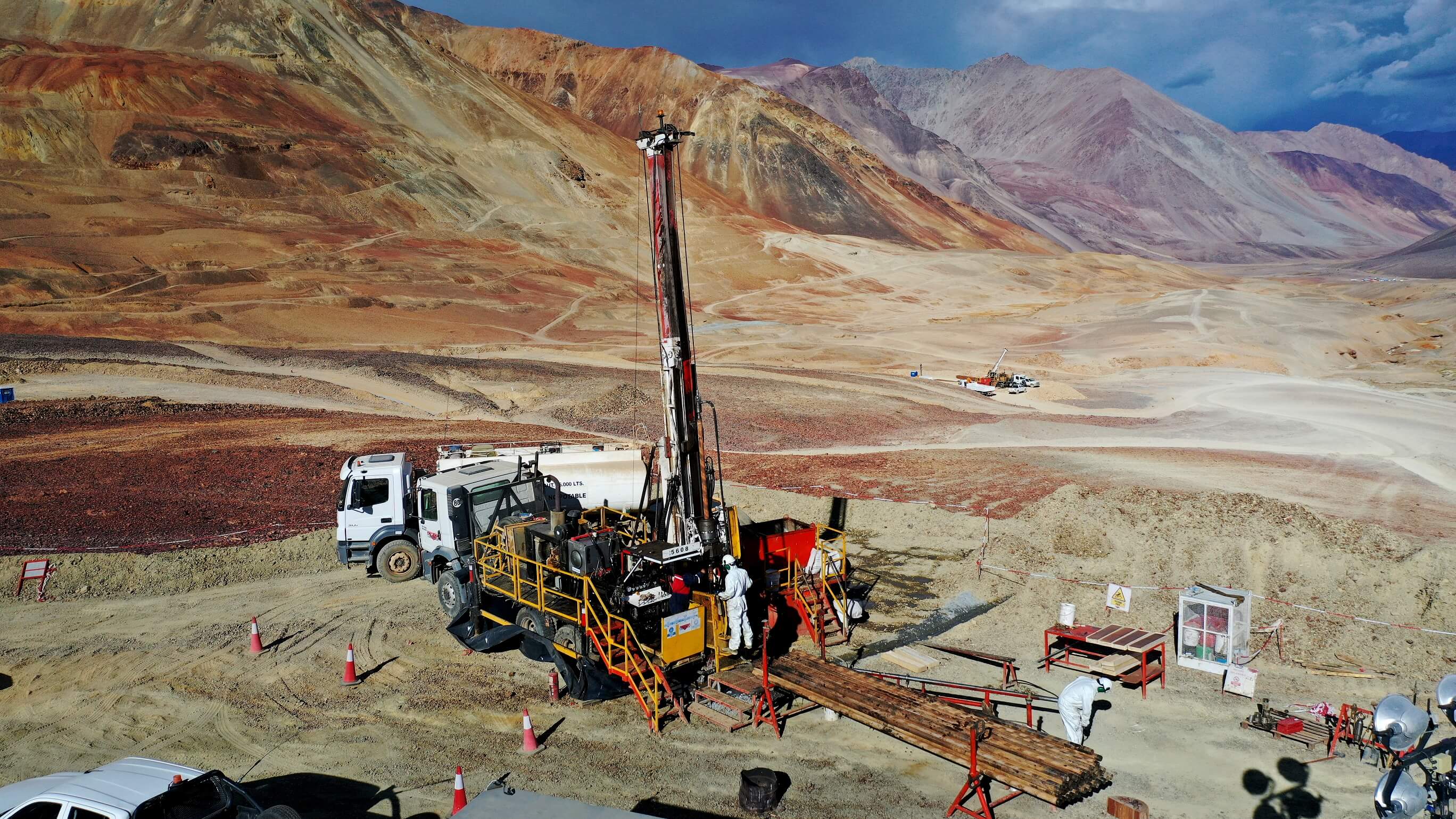
Glencore has demonstrated a sustained commitment to El Pachón and the San Juan community, especially in the Calingasta department where it operates. Its interest is evident not only in terms of investment but also in job creation and community welfare. Currently, we are working on feasibility and a robust Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA). In terms of investment, as of December 2023, El Pachón invested US$124.3 million. For the current year and until June 2024, El Pachón expects to make an approximate investment of US$98.4 million in early works, access roads, engineering studies, and geotechnical and hydrogeological campaigns.
Unlike MARA, how are the challenges associated with infrastructure and logistics considered for El Pachón?
MARA and El Pachón are two distinct projects, each with its own particularities, challenges, and specific potentials. Currently, El Pachón is in the feasibility stage and is finalizing a robust EIA. MARA, on the other hand, benefiting from the Alumbrera project's infrastructure, is in the evaluation stage to determine the best development options for the project. El Pachón and MARA share the common potential to become significant copper producers, presenting a tremendous opportunity for Argentina, the provinces in which they are located, and their communities.
What conclusions can be drawn from the community work carried out in the Calingasta department over the years?
After 15 years of uninterrupted work in Calingasta, we can affirm that the community appreciates the open, constant, and transparent communication maintained by the El Pachón team. From 2019 to the present, El Pachón has invested US$1.3 million in more than 100 initiatives and community programs focused on strengthening pillars such as education, health, productive processes, and social infrastructure, positively impacting around 7,000 residents of Calingasta. One of our main strengths at El Pachón has been continuous work alongside the community, always maintaining an open-door policy for those with inquiries, doubts, proposals, or ideas to discuss with the team. Sometimes, these discussions lead to the realization of social projects, while in other cases, there may be uncertainty, but we are always ready for dialogue and to inform the processes the project is undergoing. To build an enriching relationship with the community that allows for the development not only of our activity but also of all productive and social initiatives, it is essential to be integrated and understand their expectations to tackle the various challenges together.
How would efficient water management be implemented in both projects, considering they are located in desert environments?
We understand mining from a sustainability perspective where responsibility and good practices are indispensable. Therefore, we focus on maintaining the highest level of care for people and natural resources and contributing to the well-being of communities near the project. Glencore recognizes access to clean and safe water and sanitation as a human right since it is a shared and finite resource; hence, we ensure efficient use of the resource and apply innovative technology for water recirculation and evaporation reduction.
In the case of MARA and El Pachón, efficient water use management is achieved through project engineering development. This is where the components for water management are defined. Some of these components include the milling sector, the flotation plant, the tailings thickener sector, and the tailings deposit. Each of these components is designed to optimize water use and retain it in an internal circuit for reuse, thus reducing the extraction of this resource from the environment and, consequently, the water footprint of the projects. Furthermore, projects of El Pachón and MARA's magnitude, coupled with Glencore's high standards, require guidance from international norms, which demand exhaustive baseline studies and the analysis of water quality and aquifer flow behavior at the basin or regional level. It also requires the development of high-level management plans and the most appropriate mitigation measures.
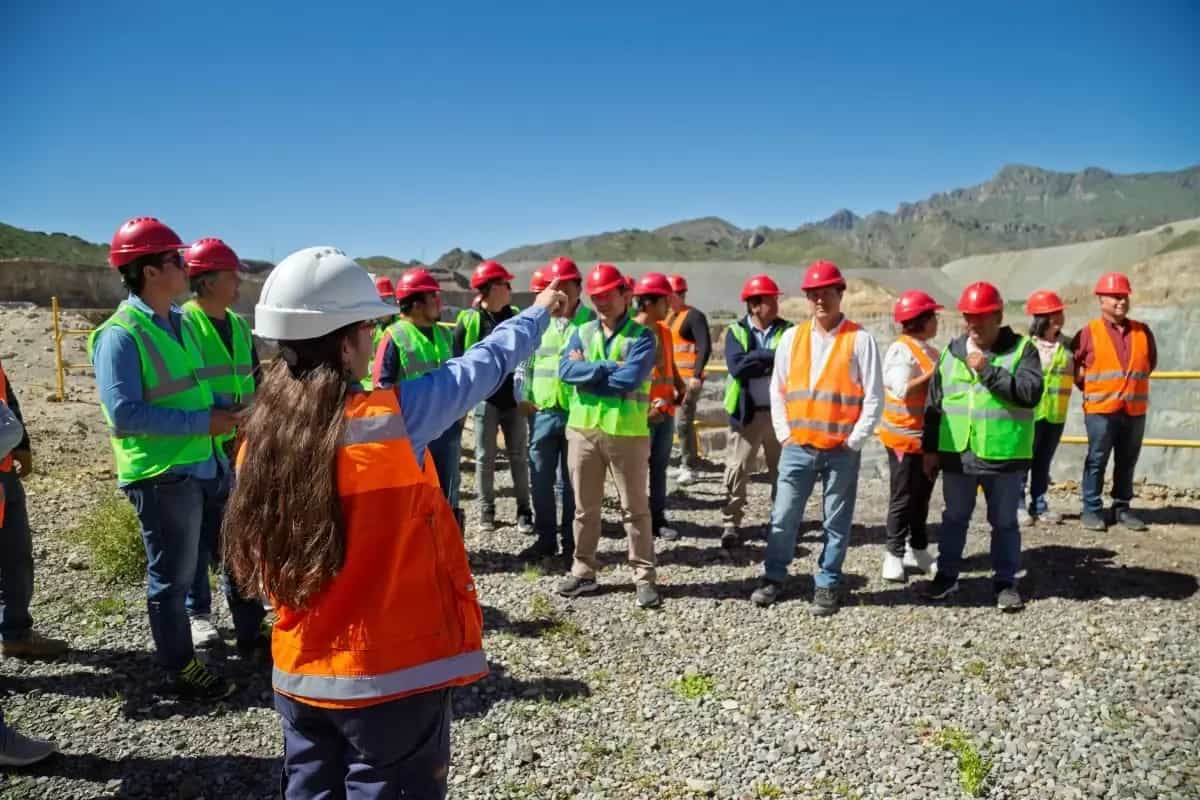
The implementation of projects as significant as MARA and El Pachón would require thousands of people. Has the company engaged in joint developments in training and education – both university-level and vocational – with provincial authorities?
In both MARA and El Pachón, alternatives for developing the competencies and skills required by both projects are being explored. Although still in the planning and evaluation stage, these strategies include several parallel alternatives involving collaboration with provincial universities, technical schools, provincial authorities of Education and Mining, unions, other mining companies and projects, specialized consultants from the region, and business associations.
In the case of MARA, the company has already undertaken significant initiatives in the past and continues to promote activities for this purpose, such as summer internships for students in various areas. In San Juan, a clear example of where this collaborative approach is heading was the recent development of the seminar "The challenge of developing mining competencies for San Juan, 2025-2035", organized in November 2023 by the National University of San Juan together with Glencore Pachón. It was a highly enriching event that involved the university's rector, authorities, and academic staff; officials from the San Juan government; mining projects and companies such as Josemaría, Los Azules, Gualcamayo, and Filo del Sol; representatives from the AOMA and UOCRA unions of San Juan; the San Juan Mining Chamber, and members of the Federico Salvio Technical School (from Calingasta).